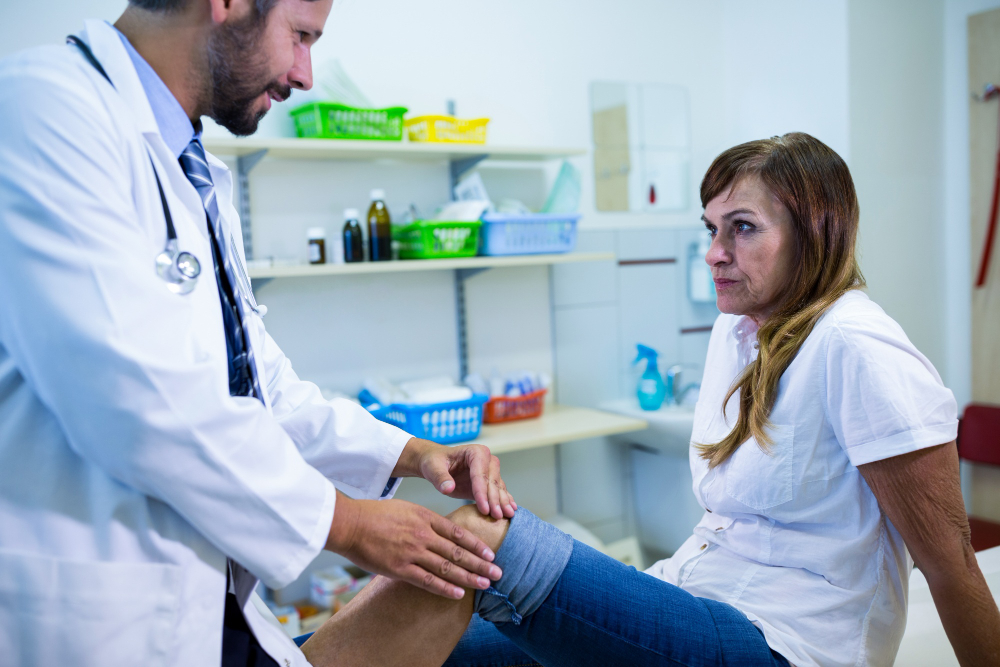
Evaluation and Preoperative Planning:
The process begins with a thorough evaluation of the patient’s knee condition by an orthopedic surgeon. This assessment involves physical examinations, medical history review, imaging studies (X-rays, MRI, CT scans), and functional assessments to determine the extent of knee damage and the suitability for robotic knee replacement. Preoperative planning is crucial, where the surgeon uses advanced imaging and robotic software to create a personalized surgical plan based on the patient’s unique anatomy.
Surgical Procedure:
On the day of the surgery, the patient is taken to the operating room, where they are administered anesthesia. The surgeon then uses the robotic system to execute the preoperative plan, which guides the precise removal of damaged bone and cartilage and the placement of the artificial knee components. Throughout the procedure, the robot assists the surgeon in achieving optimal alignment and balance of the knee joint, leading to improved implant positioning and stability.
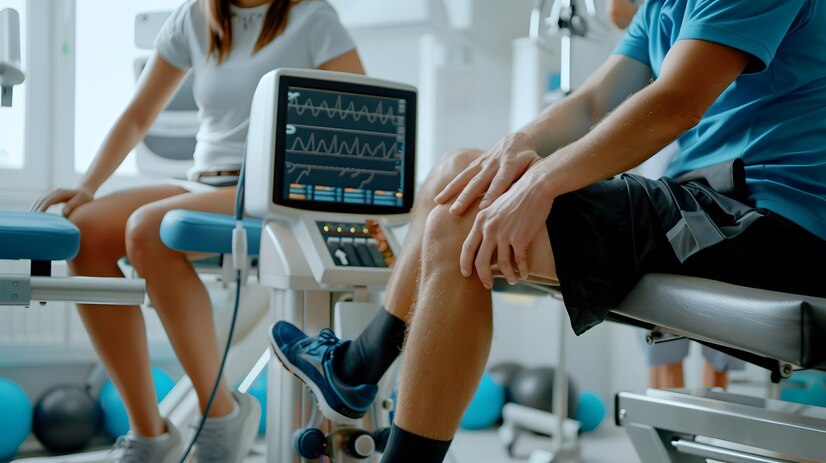
Postoperative Recovery:
After the surgery, the patient is moved to the recovery room and monitored closely. The length of hospital stay may vary depending on individual cases and the surgical approach. In many cases, patients can expect a shorter hospital stay and a faster recovery compared to traditional knee replacement surgery due to the minimally invasive nature of the robotic procedure.
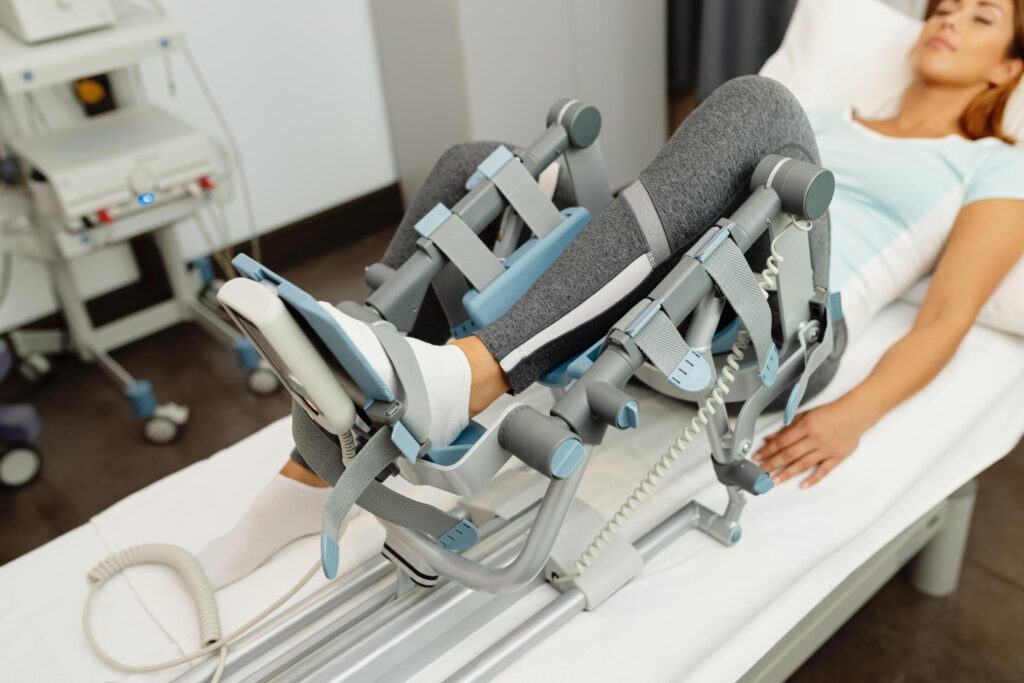
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy:
Following robotic knee replacement, the patient is encouraged to engage in physical therapy and rehabilitation to regain knee strength, mobility, and function. A customized rehabilitation plan is designed to address individual needs, gradually progressing from basic exercises to more complex activities. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in facilitating a full and successful recovery.
Postoperative Follow-Up:
Regular postoperative check-ups are essential to monitor the healing process, assess the patient’s progress, and address any concerns or complications that may arise. The surgeon and healthcare team closely monitor the patient’s recovery, providing necessary guidance and support throughout the rehabilitation period.
Long-Term Maintenance:
While the surgery can provide substantial relief from knee pain and improve mobility, it is crucial for patients to maintain a healthy lifestyle and follow their surgeon’s recommendations for long-term success. Activities that put excessive stress on the knee joint should be avoided, and patients are encouraged to engage in low-impact exercises to preserve the longevity of the knee replacement.
Potential Revision:
In some cases, a revision knee replacement may be required if there are complications or wear and tear over time. The decision for revision surgery is carefully assessed by the surgeon based on the patient’s condition and needs.
